MySQL Scalability Practice
Agenda
Ø Brief Introduction
Ø High Availability and Scalability
Ø MySQL Replication
Ø MySQL Cluster
Ø DRBD
Ø Resources
MySQL Brief introduction
Ø High performance
Ø Reliable
Ø Easy To Use
High Availability
• 7 * 24 * 365 online
• Single point of failure
• Auto Recover
Scalability
• Scalability refers to the ability to spread the load of your application queries across multiple MySQL servers.
Scalability - Scale up
• Scale vertically - add resources to a single node in a system, typically involving the addition of CPUs or memory to a single computer.
• Pros :
ü Simple Maintenance
ü Centralization Data, Simple application architecture
• Cons :
ü Expensive Device
ü Limitation of processing, Prone to bottleneck
ü Single point of failure
Scalability - Scale out
• Scale horizontal - add more nodes to a system, such as adding a new computer to a distributed software application.
• Pros :
ü Bottleneck is not easy occur
ü Low cost device.
ü Little impact on single point of failure, HA
• Cons :
ü More nodes, more complex
ü Difficult to maintain
Scalability - Scale out
• Database Scale out How?
Scalability – Principle
• Principle :
Ø Minimize Transaction Relevance
Ø Data Consistency, BASE model
Ø HA、Data Security. Data Redundancy.
MySQL Replication
Features :
o Across different platforms
o Asynchronous
o One master to any number of slaves.(separate R/W)
o Data can only be written to the master
o No guarantee that data on master and slaves will be consistent at a given point in time.
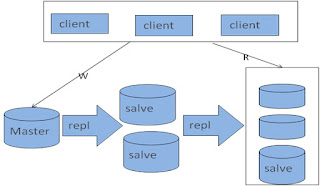
MySQL Replication – Process
Master
• I/O thread
• Binary Log (mysqld log-bin)
Slave
• I/O thread
• SQL thread
• Relay Log
• Master-info
MySQL Replication – Level
Ø Statement Level
Ø Row Level (support from 5.1.5)
MySQL Replication – Architecture
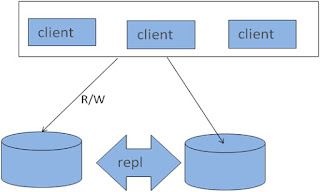
• Master-slaves
MySQL Replication – Architecture
• Master – Master
MySQL Replication – Architecture
• Master-Slaves-Slaves
MySQL Replication - Architecture
MySQL Replication – Architecture
MySQL Replication – Architecture
Sharding
Ø Vertical Sharding
• according to function, different table locate on different DB
Ø Horizontal Sharding
• data on same table locate on different DB
Ø Mixed Sharding
• Pros and Cons
Application System How to integrate all of data source?
Ø Each application system maintain its required data sources
Ø Unified management by middle layer
o Self-developed
o MySQL Proxy(connection route, load balance, HA query filter query modify)
o Amoeba,based on java
o HiveDB
Sharding Problems
Ø Distribute transaction question
Ø Join cross multi nodes(supported by federated storage engine)
Ø Merge sort paging cross multi nodes
Ø Real-time transactional relational
Ø “Shared-nothing" distributed architecture
Ø No single point of failure, two replicas is needed
Ø Synchronous and two-phase commit
Ø R/W on any nodes
Ø Automatic failover between nodes
Shared-Nothing
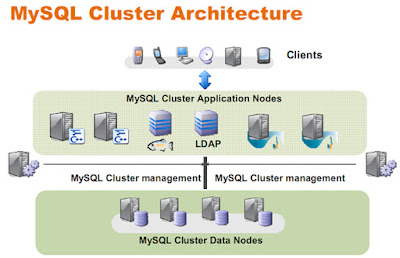
MySQL Cluster
MySQL Cluster
• Three parts:
Ø Manage node
Ø SQL node, startup with ndbcluster
Ø NDB data node
• Data storage and management of both in-memory and disk-based data
• Automatic and user defined partitioning of data
• Synchronous replication of data between data nodes
• Transactions and data retrieval
• Automatic fail over
• Resynchronization after failure
MySQL Cluster
MySQL Cluster
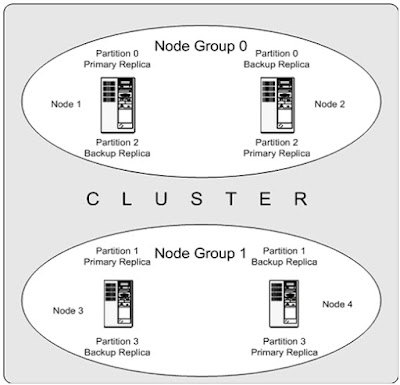
Ø Cluster Nodes
Ø Node Groups
[number_of_node_groups] = number_of_data_nodes / NumberOfReplicas
Ø Replicas
The number of replicas is equal to the number of nodes per node group
Ø Partitions
This is a portion of the data stored by the cluster
MySQL Cluster normally partitions NDBCLUSTER tables automatically Horizontal Data Partitioning. Based on hash algorithm based on the primary key on the table.
MySQL Cluster
MySQL cluster replication
Replicate asynchronously
DRBD (Distributed Replicated Block Device)
DRDB is a solution from Linbit supported only on Linux. DRBD creates a virtual block device (which is associated with an underlying physical block device) that can be replicated from the primary server to a secondary server.
MySQL HA
Resources
Ø HA: Heartbeat
Ø Load balance : F5/NetScalar/LVS/HAProxy
Ø Monitor : Nagios/cacti












This blog is so nice to me. I will keep on coming here again and again. Visit my link as well.
ReplyDeleteHibernate Training in Chennai
Spring and Hibernate Training
Hibernate Training in Porur
Spring Training in Chennai
Core Spring Training
soft skills training in chennai
core java training in chennai
Hibernate Training in T Nagar
Wonderful Article. Thanks for sharing this post
ReplyDeleteSite Reliability Engineering Training
SRE Training in Hyderabad
Site Reliability Engineering Training in Hyderabad
Site Reliability Engineering Online Training
Site Reliability Engineering Training Institute in Hyderabad
SRE Training Course in Hyderabad
SRE Online Training in Hyderabad